Amid the slings and arrows of outrageous fortune in the stock, bond, and commodity markets this week, a few 'rotten' things began to emerge. With major indices diverging notably, new highs and new lows soaring, and breadth deteriorating, analysts noted the re-awakening of The Hindenburg Omen signal…
As John Hussman previously wrote, when we think of market “internals,” the number of new highs and new lows can contribute useful information. To expand on the vocabulary we use to talk about internals, “leadership” typically refers to the number of stocks achieving new highs and new lows; “breadth” typically refers to the number of stocks advancing versus declining in a given day or week; and “participation” typically refers to the percentage of stocks that are advancing or declining in tandem with the major indices.
The original basis for the Hindenburg signal traces back to the “high-low logic index” that Norm Fosback created in the 1970’s. Jim Miekka introduced the Hindenburg as a daily rather than weekly measure, Kennedy Gammage gave it the ominous name, and Peter Eliades later added several criteria to reduce the noise of one-off signals, requiring additional confirmation that amounts to a requirement that more than one signal must emerge in the context of an advancing market with weakening breadth.
And this week saw renowned technician Tom McClellan declare a Hindenburg Omen had struck…
Dec. 1 was Hindenburg Omen day, a study created by the late Jim Miekka. Some signals matter a whole lot, others not so much. pic.twitter.com/7SBXLXA19Z
— Tom McClellan (@McClellanOsc) December 2, 2016
As we discussed over 6 years ago, the dreaded Hindenburg Omen is easily the most feared technical pattern in all of chartism (for the bullishly inclined). Those who know what it is, tend to have an atavistic reaction to its mere mention. Those who do not, can catch up on its implications courtesy of Wikipedia, but in a nutshell: "The Hindenburg Omen is a technical analysis that attempts to predict a forthcoming stock market crash. It is named after the Hindenburg disaster of May 6th 1937, during which the German zeppelin was destroyed in a sudden conflagration." Granted, the Hindenburg Omen is not a guarantee of a crash, and the five criteria that must be met for a Hindenburg trigger typically need to reoccur within 36 days for reconfirmation. Yet the statistics are startling: "Looking back at historical data, the probability of a move greater than 5% to the downside after a confirmed Hindenburg Omen was 77%, and usually takes place within the next forty-days."
As a reminder, the 5 criteria of the Omen are as follows:
- That the daily number of NYSE new 52 Week Highs and the daily number of new 52 Week Lows must both be greater than 2.2 percent of total NYSE issues traded that day.
- That the smaller of these numbers is greater than or equal to 69 (68.772 is 2.2% of 3126). This is not a rule but more like a checksum. This condition is a function of the 2.2% of the total issues.
- That the NYSE 10 Week moving average is rising.
- That the McClellan Oscillator is negative on that same day.
- That new 52 Week Highs cannot be more than twice the new 52 Week Lows (however it is fine for new 52 Week Lows to be more than double new 52 Week Highs). This condition is absolutely mandatory.
The last Hindenburg Omen occurred as the markets began to roll over in June 2015 (and did not end well) although that had followed a series of false alerts in the 2013 QE-enthused melt-up.
However, while McClellan called the Hindenburg, it appears it may have fallen just short…
Checking the rules:
1: YES – see chart above (red and green lines BOTH above the blue)
2: YES – 74 > 69
3: YES – 10628 to 10631 (rising)
4: YES – McClellan Oscillator -5.85 (below 0)
5: NO – 236 New Highs is more than double the 74 New Lows
And so from the most strict definition, The Hindenburg Omen did not strike this week…
But it's close and as a reminder, while no Hindenburg flashed, Dana Lyons noted both the number of New Highs and New Lows set 3-month highs just over a week ago. If that sounds odd, it is. In fact, it was only the 2nd day ever in which each set a 3-month high. And since 1970, only 18 prior days saw New Highs and New Lows set as much as a 1-month high.
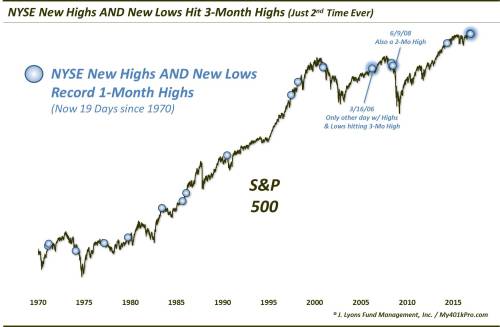
Something which has not boded well in the past…
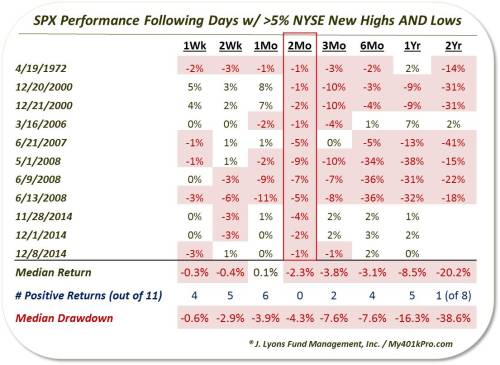
As the table shows, the return in the S&P 500 has been negative 2 months after all 11 occurrences. And it wasn’t just the 2-month period that was poor. Median returns are negative across nearly all time frames from 1 week to 2 years. The 2-year result is perhaps the most eye-opening after the 2-month. The market is not typically down over a 2-year period so to see 7 of the 8 instances lower is a rare result.
What causes the elevated numbers of New Highs and New Lows? And why would it necessarily be a negative for the stock market? We’re not sure, and we don’t really care. We’re never too concerned with the “why’s” when it comes to the markets. All we care about is what is happening. And for whatever reason, the market has been especially weak – and consistently so – following the occurrence of lots of New Highs and Lows. That is a legitimate red flag currently, in our view.
The post Did The Market Just Flash A Hindenburg Omen Warning? appeared first on crude-oil.top.


